How Children Will Shape the Future of AI

Artificial intelligence (AI) is advancing at an extraordinary pace, impacting nearly every industry and aspect of daily life. Breakthroughs in technologies like machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and robotics have transformed AI into a smarter, more efficient force capable of handling tasks once thought to be exclusively human. Today’s AI systems excel in areas such as image generation, autonomous navigation, and advanced problem-solving. In healthcare, AI not only assists in diagnosing diseases but also personalizes treatment plans. Meanwhile, in finance, AI optimizes everything from automated trading to fraud detection. These advances aren’t isolated—they’re part of a wider transformation where AI’s influence stretches across diverse fields like autonomous vehicles, creative industries, and personalized content generation. Recent innovations, such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT and DALL·E, have redefined natural language processing and image generation, creating more lifelike interactions and more creative outputs than ever before. Robotics has also seen impressive developments, with robots like Tesla’s Optimus showing promise in manufacturing, logistics, and beyond. AI is now a cornerstone of smart homes, managing everything from energy consumption to security systems. Platforms like Google Bard and AI-powered tools in platforms like Adobe Firefly are reshaping how we interact with technology, bringing AI deeper into content creation, task management, and decision-making processes. Children growing up in this AI-saturated world are uniquely positioned to shape its future. Their early exposure to AI, from interactive educational platforms to creative AI tools, equips them with the skills and perspectives necessary to influence how AI develops. As natural-born users and future creators, these children will play a crucial role in determining AI’s ethical trajectory, innovative applications, and societal impact. Here’s How Children Are Poised to Play a Significant Role in Shaping the Future of AI. 1. Early Exposure and Familiarity 2. Education and Skill Development 3. Ethical Considerations and Values 4. Innovation and Creativity 5. The Workforce of Tomorrow Conclusion Children are uniquely positioned to shape the future of AI. Their early exposure to AI, combined with their creativity and innate sense of fairness, will play a pivotal role in how AI develops across industries and societal applications. By fostering AI education, creativity, and ethical awareness in children, we can empower the next generation of innovators and leaders who will harness AI responsibly. The future of AI will not just be about technological advancement but about ensuring that AI serves humanity in a collaborative and meaningful way. By nurturing children’s relationship with AI, we can create a more equitable, creative, and sustainable world where AI enhances human potential.
The GenAI Show: Empowering the Next Generation of AI Leaders
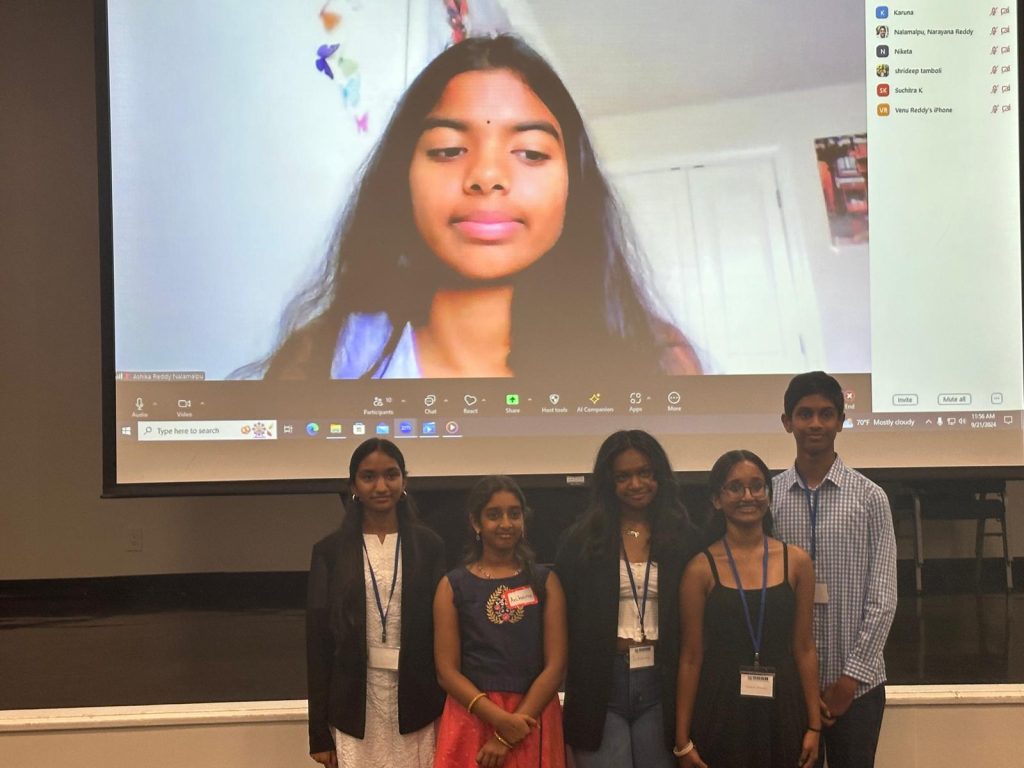

In an era where artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming industries, the ability to harness its power creatively and responsibly is becoming essential. The future of AI will be driven by today’s youth, and what we witnessed at “The GenAI Show” is a glimpse into the incredible potential of our young minds. This event was not just a competition but a celebration of creativity, innovation, and leadership — all powered by cutting-edge Generative AI tools. We are delighted to share the success of “The GenAI Show,” a unique event organized by {igebra.ai}, as part of the prestigious ASEI 36th Annual National Convention. The show provided an extraordinary platform for students from grades 7 to 12 to showcase their creative talent, their technical prowess, and their ability to adapt to the rapidly evolving AI landscape. With the guidance and support from Subba Gopavarapu and leadership from Sanjay B Dalal, Chairperson of ASEI SoCal, and G Satish, President of ASEI SoCal, the event exceeded all expectations. A Journey to Creative Mastery The GenAI Show unfolded in five meticulously planned phases: 1. Online Workshop & Support Sessions: On September 3rd and 4th, students participated in an immersive online workshop, learning the fundamentals of Generative AI in a compact 4-hour session. Delivered via Zoom, these sessions, led by the expert team at {igebra.ai}, empowered students to explore GenAI tools and develop video stories. The energy and enthusiasm from the students were infectious, and despite the short training duration, the results were astounding. 2. Video Creation by Kids & Submission of Entries: After absorbing the training, the young participants dove into creating their story videos using GenAI tools. They submitted their entries, showcasing their newfound skills, creativity, and imagination. 3. Review and Selection of Entries: A dedicated team from {igebra.ai} meticulously reviewed the submissions. The selection process was challenging, given the extraordinary quality and uniqueness of the submissions. 4. Online Semi-Finals: The semi-finalists were chosen and presented their videos in an online setting. These semi-finals set the stage for the finalists who would go on to present their creations at the national convention. 5. Finals at the ASEI National Convention: The six remarkable finalists were invited to the ASEI National Convention in Fullerton, California, on September 21st, where they presented their stories. The live audience, composed of AI leaders, entrepreneurs, and influential figures, was left in awe. The creativity, storytelling, and technical mastery of these young talents were unparalleled. Meet the Finalists: The Future of AI The theme of the competition was “The Future of AI”, and the six finalists truly embodied this topic with their creative, thought-provoking stories. Each participant brought their own perspective on how AI could shape the future, crafting narratives that captivated the audience and explored the profound impact of AI on various aspects of life. Deepshika Perumalla (7th Grade): Deepshika’s story centered around an AI teacher who transforms a small village. In her narrative, AI revolutionizes education by bringing personalized learning to children in remote areas, ultimately uplifting the entire community through knowledge and innovation. Ashika Reddy Nalamalpu (9th Grade): Ashika’s gripping story followed two siblings whose parents go missing. Using the skills and techniques they learned from their parents about handling AI systems, the siblings embark on a thrilling mission to find them. Her narrative beautifully blended adventure with the power of AI to solve problems and protect loved ones. Saanvi Katkuri (9th Grade): Saanvi’s story offered a glimpse into a day in the life of a helpful robot, designed to assist people in their daily tasks. Her video explored how robots could seamlessly integrate into human life, offering support, comfort, and practical solutions in a fast-paced world. Suyash Vakicherla (9th Grade): Suyash crafted a compelling narrative about a scientist who creates a humanoid robot. Over time, the robot learns about humans, their cultures, and emotions, highlighting the potential of AI to not only assist in practical tasks but also understand and empathize with human experiences. Archana Girish (5th Grade): The youngest finalist, Archana, told the story of a young boy who grows up with AI robots and embarks on a mission to save humans locked in a temple. With the help of his AI companions, he uses intelligence and bravery to rescue those in need, demonstrating how AI can be both a guide and a protector. Sahi Gopavarapu (9th Grade): Sahi’s story introduced “Echo,” an AI system that helps individuals balance work and family life. By managing daily tasks and responsibilities, Echo gives people more time to rejuvenate and spend with loved ones, illustrating how AI can enhance the quality of life by fostering a better work-life balance. Each of these stories painted a unique picture of how AI could transform different aspects of life, from education and family to adventure and exploration. These finalists didn’t just imagine a world with AI — they brought it to life through storytelling, demonstrating their deep understanding of AI’s potential to shape the future. An Event to Remember The GenAI Show was not just a success; it was a resounding triumph. The judges, consisting of AI experts and educators, found themselves in a difficult position as they deliberated on the winners. Each video was unique, blending technical mastery with rich storytelling, leaving the audience both inspired and amazed. In the end, three exceptional students were crowned winners, receiving recognition and rewards for their outstanding efforts. What made this event even more impressive was that these young minds learned everything in just two days. It’s a testament to their dedication, passion, and innate ability to adapt to the new era of AI. Their journey from learning GenAI tools to presenting at a national stage showcases how quickly the next generation can become leaders, creators, and innovators. The Future Is Now These young participants are not just GenAI creators; they are the AI leaders of tomorrow. The GenAI Show was a glimpse into what’s possible when we provide the right tools, mentorship, and platforms for young minds. The confidence and skills they
How Generative AI is Redefining Marketing Efforts

In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, Generative AI has emerged as a game-changer for marketing. The capacity of AI to generate creative content, streamline operations, and deliver personalized experiences is transforming traditional marketing paradigms into dynamic, efficient, and highly adaptive strategies. The recent surge in technological advancements has provided marketers with powerful tools to enhance engagement, optimize campaigns, and measure outcomes with precision, marking a pivotal shift in how brands interact with their consumer base. Here’s a deep dive into how Generative AI is redefining marketing efforts across various dimensions. 1. Content Creation at Scale One of the most significant impacts of Generative AI is its ability to produce a vast array of content quickly and efficiently. From writing blog posts, articles, and social media updates to creating engaging video scripts and email campaigns, AI tools can generate tailored content that resonates with target audiences. This capability not only speeds up the content creation but allows marketers to produce more content at a higher quality with less human input. According to Deloitte Digital, marketers who adopt generative AI have seen a 12% return on investment. The technology not only keeps up with content demands but also helps marketers stay ahead, ensuring that they can handle the increased content requirements which have grown by 54% in the last year. The arena of content marketing has been particularly revolutionized by Generative AI, with tools like OpenAI’s GPT models facilitating the automatic generation of textual content—from blog posts to complete marketing narratives. Additionally, platforms like Jasper and Writesonic are assisting marketers in scaling their content production without compromising on quality, thereby driving better engagement and ROI. 2. Personalization Generative AI excels in understanding and predicting consumer behavior based on data. By analyzing customer interactions, preferences, and feedback, AI can help marketers craft highly personalized content and offers. This level of personalization is key to enhancing customer engagement, improving conversion rates, and building lasting relationships with consumers. AI tools now offer deep personalization across various customer touch points. For example, new features from Google aim to enhance the shopping experience by creating more effective product imagery and immersive ad formats, deepening the connections between shoppers and brands. Similarly, Salesforce notes that 68% of service professionals use generative AI to create and personalize service communications, significantly enhancing customer interactions and automating service communications 3. Visual Content Development AI is not just revolutionizing textual content but is also making strides in visual marketing. Generative AI tools can now design graphics, edit photos, and even create entire video sequences, tailored to specific marketing campaigns. Tools like Adobe Firefly and Canva’s Magic Write harness AI to automate the design process, enabling the creation of sophisticated graphic designs and imagery with minimal human input. These platforms use AI to suggest design elements based on the content’s context and the brand’s style, making it easier for marketers to maintain visual consistency across their digital assets. Generative AI technology has significantly simplified video production and editing, a traditionally time-consuming and resource-intensive task. Platforms such as Synthesia and Lumen5 leverage AI to automate video creation, from scriptwriting to scene layout and final editing. These tools can generate promotional videos, tutorials, and social media video posts that are customized to a brand’s requirements and audience preferences. These tools are equipped to maintain brand consistency in visuals while adapting designs to suit different platforms and devices, significantly reducing the workload of human designers. 4. Predictive Analytics and Decision Making Generative AI goes beyond creation and into the realm of analytics and strategic decision-making. By processing large datasets, AI can predict trends, customer behavior, and the potential success of marketing campaigns. This predictive capability enables marketers to make data-driven decisions, optimize their strategies in real-time, and allocate resources more effectively. Tools Enhancing Predictive Analytics 5. Enhanced Customer Interactions Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by Generative AI are transforming customer service and support. These AI solutions can handle inquiries, resolve issues, and provide information around the clock without human intervention. They can also learn from interactions to improve their responses over time, providing a seamless and personalized customer experience. 6. SEO and Online Visibility Generative AI tools are also enhancing Search Engine Optimization (SEO) efforts. They can analyze search engine algorithms, suggest relevant keywords, optimize website content, and even generate SEO-friendly titles and meta descriptions. This helps improve the visibility of brand content in search engine results, attracting more organic traffic to websites. Generative AI tools like Clearscope and MarketMuse are transforming SEO by analyzing competitor content and providing actionable insights for content improvement. These tools help identify keyword opportunities, optimize content structure, and predict the potential success of articles, contributing to better rankings and increased organic traffic. According to industry studies, the use of AI in SEO can improve organic traffic by as much as 47%, with tools like CanIRank offering specific recommendations by comparing user content with top-ranking posts. Moreover, AI-driven SEO tools automate many aspects of content optimization such as suggesting the optimal length, structure, and keyword placement, which are crucial for ranking well in search engines. They also provide real-time adjustments based on search engine algorithm updates and changing user behaviors, ensuring that SEO strategies remain effective and current. As AI continues to evolve, its role in enhancing online visibility through strategic, data-driven insights becomes increasingly indispensable for marketers aiming to achieve and maintain top search engine rankings. Ethical Considerations and Challenges Generative AI in marketing introduces significant ethical considerations and challenges that need thoughtful attention. Key concerns include data privacy and the potential for bias in AI algorithms. It’s crucial for marketers to ensure compliance with data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA by obtaining consent and anonymizing data. Furthermore, mitigating biases in AI outputs is essential, requiring diverse data sets and ongoing monitoring to promote fairness. The technology’s capacity to generate authentic-seeming content also raises issues of misinformation, necessitating a commitment to truthfulness and ethical guidelines to maintain the integrity of marketing campaigns. Moreover, as AI automates tasks traditionally
The Transformative Impact of Generative AI in the Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry is witnessing a seismic shift, driven by the integration of advanced technologies such as Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI). This technology is not merely a tool for improvement but a transformative force redefining the scope of production capabilities, efficiency, and innovation. The statistical impact of Generative AI on manufacturing growth is both profound and quantifiable, indicating significant advancements in sector efficiency: These metrics underscore the substantial role that Generative AI plays in enhancing manufacturing outcomes, making it a cornerstone of modern industrial strategies. The Role of Generative AI in Manufacturing Innovating Product Design The product design process has been radically transformed by Generative AI. Traditionally, product design was a linear and iterative process that required extensive time and resources to move from concept to prototype, with designers manually sketching ideas, creating models, and testing prototypes. This process could take several months to years depending on the complexity of the product. However, with the advent of Generative AI, the design process has become highly dynamic and efficient. AI algorithms can quickly generate multiple design alternatives based on specific criteria such as durability, cost, and material usage. This not only speeds up the design phase but also allows for the exploration of more innovative and complex solutions that optimize the use of resources. A notable example is Airbus, which has utilized generative design to create aircraft parts that are significantly lighter, thus reducing material costs and enhancing fuel efficiency. Streamlining Production Lines Generative AI has similarly revolutionized production lines, which were previously reactive, managed based on predetermined schedules, or in response to machine failures. This often led to unexpected downtime, inefficiencies, and high maintenance costs. Now, production lines have been transformed into predictive and highly efficient systems through the use of Generative AI. AI-driven algorithms analyze production data in real-time to predict maintenance needs and optimize production schedules. This proactive approach significantly reduces downtime by up to 45% and enhances productivity, allowing for smoother and more cost-effective operations. Enhancing Quality Control Quality control in manufacturing has also seen a major overhaul with the adoption of Generative AI. Previously, this area heavily relied on human inspection and manual testing, which could be inconsistent and often failed to catch all defects. The traditional approach frequently resulted in higher scrap rates and inconsistent product quality. Today, with Generative AI, quality control processes have become more accurate and consistent. AI systems equipped with advanced imaging and data analysis tools can inspect products at a much higher throughput than human inspectors, with significantly greater accuracy. This technology ensures that every product meets strict quality standards, significantly reducing waste and increasing customer satisfaction. Time Savings in Production and Design Traditionally, the production and design phases in manufacturing were notably time-consuming. The cycle began with manual drafting and moved through various stages of prototyping and adjustments. Each iteration required additional time for evaluation and redevelopment, which often extended the timeline from concept to market considerably. However, the advent of Generative AI has dramatically transformed these processes. By enabling rapid prototyping and real-time adjustments, Generative AI has significantly compressed the development cycle. AI algorithms are now capable of running thousands of simulations to predict how designs will perform under various conditions, effectively reducing months of testing into mere days or hours. This acceleration is particularly evident in the automotive industry, where manufacturers have cut the design time for new vehicle parts by up to 70%. This is achieved through the use of AI-driven tools that automate and swiftly optimize design parameters, streamlining the entire process from concept to production. Enhancing Ability to Meet Supply Demands Traditionally, meeting fluctuating market demands posed a significant challenge for manufacturers, as traditional setups offered limited flexibility to scale production up or down based on real-time demand without incurring substantial costs. This often resulted in either excess inventory or supply shortages, affecting overall market responsiveness and operational costs. The integration of Generative AI has dramatically enhanced manufacturing agility, enabling factories to respond more effectively to market demands. By combining AI with advanced analytics, manufacturers can now predict demand trends more accurately and adjust production schedules accordingly without compromising operational efficiency. This responsive approach not only ensures a more reliable supply chain but also significantly reduces inventory costs and minimizes waste, aligning production more closely with actual market needs and reducing the environmental impact of overproduction. A prominent example of Generative AI’s impact can be seen in the electronics industry, where AI-driven systems forecast demand surges for new gadgets and adjust production lines in real-time to meet this demand. This capability was crucial during product launches and peak shopping seasons, where timely supply is critical for capitalizing on market opportunities. Conclusion Generative AI is redefining the manufacturing industry by enhancing efficiency, quality, and innovation. Its ability to transform data into actionable insights is proving indispensable in creating more agile, innovative, and customer-focused manufacturing processes. As we look to the future, the role of Generative AI in manufacturing is poised to grow, continually pushing the boundaries of what is possible in this dynamically evolving industry. This ongoing integration of AI promises to not only enhance manufacturing capabilities but also to drive significant economic growth in the sector.
How Will AI Affect Jobs: A Comprehensive Look at the Future of Work

The rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to spark significant discussions about the future of work. According to a report by Goldman Sachs, AI could replace the equivalent of 300 million full-time jobs by 2030. This transformation is expected to replace a quarter of work tasks in the US and Europe, signaling a shift that may also bring about new jobs and a productivity boom. The total annual value of goods and services produced globally could increase by 7%. However, the report also highlights a concerning trend: two-thirds of jobs in the U.S. and Europe are exposed to some degree of AI automation, with about a quarter potentially being fully automated. Impact of AI on Specific Job Roles By 2025, the World Economic Forum predicts that artificial intelligence will displace approximately 85 million jobs. Additionally, Freethink reports that as much as 65% of retail positions could be automated by then, attributing this shift primarily to technological progress, increasing costs and wages, tight labor markets, and decreased consumer spending. Learning Skills to Thrive with New Technology In the context of the rapid integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into various job sectors—as discussed in the previous analysis on AI’s impact on jobs by 2025—it’s crucial for today’s workforce to adapt and prepare for the changes AI will bring. Here are strategies and insights on how individuals can embrace AI and develop the necessary skills to harness this technology effectively. Conclusion: As AI reshapes our work landscape, the challenge is not just to adapt, but to thrive. The displacement of jobs by AI by 2030 underscores a critical need for skill adaptation and continuous learning. In this era of transformation, success lies in leveraging AI to enhance our capabilities and discover new career paths. Embracing AI involves more than understanding its impact; it requires a proactive approach to education and skill development. By cultivating a combination of technical know-how and enhanced soft skills, workers can not only survive but excel in an AI-integrated job market. The future of work with AI is an opportunity to innovate and improve productivity, urging us to redefine our roles and contribute to a tech-driven economy. It’s a call to action for all professionals to engage with AI positively and constructively, ensuring a future where technology and human ingenuity coexist harmoniously.
Exploring the History and Evolution of AI
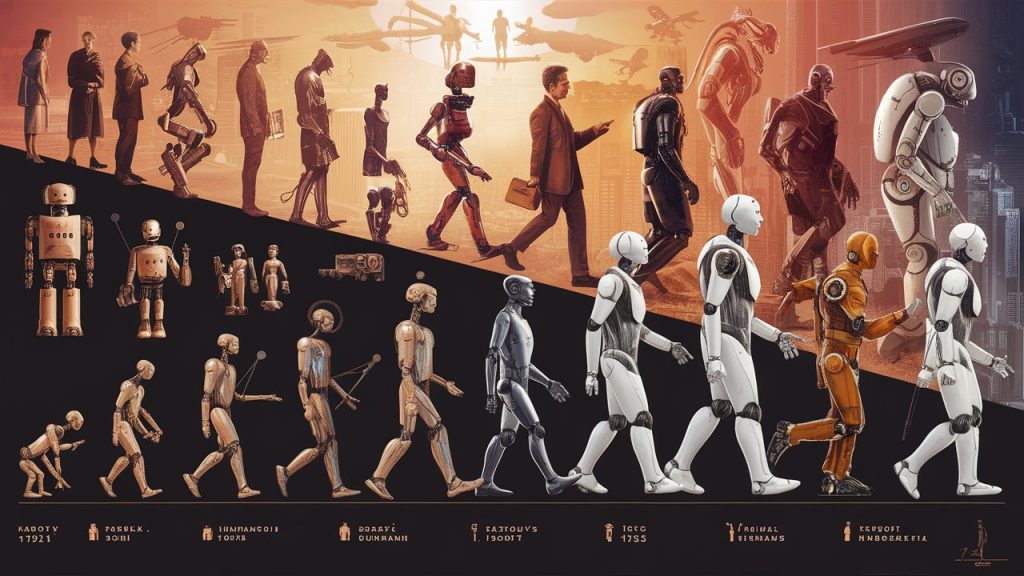

Artificial intelligence is a specialty within computer science that is concerned with creating systems that can replicate human intelligence and problem-solving abilities. They do this by taking in a myriad of data, processing it, and learning from their past in order to streamline and improve in the future. A normal computer program would need human interference in order to fix bugs and improve processes. The History of Artificial Intelligence: The idea of “artificial intelligence” goes back thousands of years, to ancient philosophers considering questions of life and death. In ancient times, inventors made things called “automatons” which were mechanical and moved independently of human intervention. The word “automaton” comes from ancient Greek, and means “acting of one’s own will.” One of the earliest records of an automaton comes from 400 BCE and refers to a mechanical pigeon created by a friend of the philosopher Plato. Many years later, one of the most famous automatons was created by Leonardo da Vinci around the year 1495. So while the idea of a machine being able to function on its own is ancient, for the purposes of this article, we’re going to focus on the 20th century, when engineers and scientists began to make strides toward our modern-day AI. Groundwork for AI 1900-1950: In the early 1900s, there was a lot of media created that centered around the idea of artificial humans. So much so that scientists of all sorts started asking the question: is it possible to create an artificial brain? Some creators even made some versions of what we now call “robots” (and the word was coined in a Czech play in 1921) though most of them were relatively simple. These were steam-powered for the most part, and some could make facial expressions and even walk. Notable Dates Birth of AI: 1950-1956 This range of time was when the interest in AI really came to a head. Alan Turing published his work “Computer Machinery and Intelligence” which eventually became The Turing Test, which experts used to measure computer intelligence. The term “artificial intelligence” was coined and came into popular use. Notable Dates AI Maturation: 1957-1979 The time between when the phrase “artificial intelligence” was created, and the 1980s was a period of both rapid growth and struggle for AI research. The late 1950s through the 1960s was a time of creation. From programming languages that are still in use to this day to books and films that explored the idea of robots, AI became a mainstream idea quickly. The 1970s showed similar improvements, such as the first anthropomorphic robot being built in Japan, to the first example of an autonomous vehicle being built by an engineering grad student. However, it was also a time of struggle for AI research, as the U.S. government showed little interest in continuing to fund AI research. AI Boom: 1980-1987 Most of the 1980s showed a period of rapid growth and interest in AI, now labeled as the “AI boom.” This came from both breakthroughs in research, and additional government funding to support the researchers. Deep Learning techniques and the use of Expert System became more popular, both of which allowed computers to learn from their mistakes and make independent decisions. Notable Dates AI Winter: 1987-1993 As the AAAI warned, an AI Winter came. The term describes a period of low consumer, public, and private interest in AI which leads to decreased research funding, which, in turn, leads to few breakthroughs. Both private investors and the government lost interest in AI and halted their funding due to high cost versus seemingly low return. This AI Winter came about because of some setbacks in the machine market and expert systems, including the end of the Fifth Generation project, cutbacks in strategic computing initiatives, and a slowdown in the deployment of expert systems. AI Agents: 1993-2011 Early 90s showed some impressive strides forward in AI research, including the introduction of the first AI system that could beat a reigning world champion chess player. This era also introduced AI into everyday life via innovations such as the first Roomba and the first commercially-available speech recognition software on Windows computers. The surge in interest was followed by a surge in funding for research, which allowed even more progress to be made. Notable Dates Artificial Intelligence is Everywhere: 2012 – Present That brings us to the most recent developments in AI, up to the present day. We’ve seen a surge in common-use AI tools, such as virtual assistants, search engines, etc. This time period also popularized Deep Learning and Big Data. Notable Dates Generative AI: Generative AI made significant strides in 2023, with the emergence of various models like Meta’s LLaMA 2, Google’s Bard chatbot, Baidu’s Ernie Bot, and OpenAI’s GPT-4. Despite initial hype, the year saw a focus on understanding the limitations and potential of generative AI, aiming to integrate it into practical applications for productivity enhancement. Augmented Reality (AR) and Quantum Computing: Alongside AI, other technologies like AR and quantum computing also saw significant advancements in 2023. AR technologies, such as Apple’s Vision Pro headset, and quantum computing developments like IBM’s System Two and Heron quantum chip, marked notable progress in their respective fields, hinting at a future where these technologies could play a more integrated role in everyday life Examples of AI Systems The global artificial intelligence market is over $136.6 billion, while the AI industry is expected to grow by 13x in the next seven years with a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 38.1%. Another report shows that 87% of global companies think AI gives them a competitive edge in the market. Be it in our personal or professional life, we cannot avoid using AI products in some form. AI has already made a positive impact across a broad range of industries. It can automate processes to free employees of unnecessary labor, provide personalized learning options for students, enable cybersecurity companies to deploy faster solutions and help fashion companies design better-fitting clothing for their customers.
How OpenAI is Pushing Boundaries in the World of Generative AI

OpenAI stands at the vanguard of artificial intelligence research and development, consistently breaking new ground with its generative AI technologies that push the boundaries from revolutionizing natural language processing with GPT-4 to enhancing image generation capabilities through DALL-E 2, OpenAI remains at the forefront of innovation, enabling profound changes across various industries. Founded with the ambitious goal of ensuring artificial general intelligence (AGI) benefits all of humanity, OpenAI has consistently pushed the boundaries of what AI can achieve. As OpenAI continues to innovate, it remains acutely aware of the ethical dimensions of AI development. The organization’s approach to deployment emphasizes safety, transparency, and alignment with human values, ensuring that its technologies do not just advance human capability but also enhance human well-being. This blog delves into the recent breakthroughs by OpenAI, exploring how its cutting-edge technologies are being integrated across various sectors and what these advancements signify for the future of AI. A Brief History of OpenAI OpenAI, since its inception in December 2015, has played a pivotal role in reshaping the landscape of artificial intelligence. Founded by Elon Musk, Sam Altman, Greg Brockman, Ilya Sutskever, Wojciech Zaremba, and John Schulman, the organization was established with the ambitious goal of promoting and developing friendly AI in a manner that benefits humanity as a whole. Initially launched as a non-profit, OpenAI aimed to freely collaborate with other institutions and researchers by making its patents and research open to the public. The organization quickly became renowned for its significant contributions to the AI field, particularly through its development of advanced deep learning models. In 2018, OpenAI transitioned to a “capped-profit” model to attract outside investment while still pursuing its original mission of safe and beneficial AI. This move was pivotal in scaling its ambitions and projects, culminating in securing a $1 billion investment from Microsoft in 2019. One of OpenAI’s most notable innovations is the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) series, starting with the release of GPT in 2018, followed by more sophisticated versions—GPT-2 in 2019, and GPT-3 in 2020. These models demonstrated unprecedented capabilities in natural language processing, setting new standards for AI applications in writing, conversation, and even coding. In 2021, OpenAI expanded its technological repertoire with the introduction of DALL-E, an AI program capable of generating images from textual descriptions, and Codex, which powers GitHub’s Copilot, assisting programmers by suggesting lines of code. These advancements showcased OpenAI’s commitment to diversifying the applications of AI. By 2024, OpenAI further enhanced its offerings with the launch of GPT-4 and GPT-4o, pushing the boundaries of language models with even greater speed, accuracy, and multimodal capabilities. These versions improved interactions in over 50 languages and introduced capabilities in text, voice, and vision, making advanced AI tools more accessible to a broader range of users and applications. Alongside its technological advancements, OpenAI continued to emphasize the importance of ethical AI development, focusing on safety, transparency, and alignment with human values to ensure that AI advancements contribute positively to societal welfare. Recent Developments in OpenAI’s Generative AI Leveraging the foundational technologies of DALL-E and GPT models. In preparation for its release, OpenAI is conducting rigorous safety evaluations of Sora, including adversarial testing to address potential issues like misinformation, hateful content, and bias. This proactive approach ensures that Sora not only enhances creative possibilities but also adheres to ethical standards. By simulating real-world dynamics, Sora is positioned as a cornerstone for future models that aim to understand and interact with the world, marking a crucial step towards the goal of achieving artificial general intelligence (AGI). Future Directions Looking ahead, OpenAI is not just pushing technological boundaries but also focusing on how these technologies can be safely integrated into society. They are working on improving the accessibility of AI tools so that more individuals and businesses can benefit from AI technology, while also addressing concerns about job displacement and privacy. OpenAI’s continuous innovations in generative AI are transforming industries and changing our perception of what artificial intelligence can achieve. As we move forward, the potential applications of AI seem almost limitless, promising a future where AI assists in fostering creativity, problem-solving, and perhaps most importantly, an understanding of our own human condition.
Will GenAI Make Human Creativity Obsolete?

As we delve deeper into the 21st century, the rapid evolution of artificial intelligence, especially generative AI (GenAI), is reshaping numerous facets of human life. GenAI’s capabilities in emulating and even surpassing certain aspects of human creativity have sparked a vibrant debate about its implications for the future of creative professions. With GenAI’s ability to produce compelling art, write engaging narratives, and generate functional code, there’s growing concern and curiosity about the role of human creativity in a world where machines can mimic this distinctly human trait. But is human creativity really at risk of becoming obsolete, or are we entering a new era of augmented creativity? Understanding GenAI Generative AI tools have been designed to create new content—ranging from text and images to music and software code—based on vast datasets they have been trained on. Notable examples include GPT for text generation and DALL-E for image creation, which have showcased the potential of AI to perform tasks traditionally deemed as creative. These tools not only mimic existing styles but also generate novel content, opening up a plethora of possibilities across various domains. The Impact on Creative Industries The influence of GenAI in creative fields is undeniable. The GenAI’s integration is multifaceted and growing. Let’s explore its impact across various roles: 1. Graphic Designing: AI tools can now automate routine aspects of design and help in creating complex visual effects, providing designers with more space to focus on innovative design concepts. Before AI: Traditionally, graphic designers would manually create every element of 1a design using software like Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator. This process could be time-consuming, requiring extensive effort for revisions and adjustments based on client feedback. After AI: With AI tools such as Adobe Sensei and more specialized image generation tools like DALL-E or Midjourney, designers can automate routine tasks like resizing and color adjustments and also generate complex images from textual descriptions. These tools enable designers to quickly prototype and iterate on visual concepts, allowing for a dramatic increase in creative possibilities and efficiency. They can also experiment with new styles and visual ideas that may have been impractical or overly time-consuming to explore manually. 2. Video Editing: AI can drastically reduce the time needed for editing by automating cuts, transitions, and effects based on the editor’s style, allowing more time for creative storytelling. Before AI: Video editors would sift through hours of footage, manually selecting clips and applying transitions and effects. Tools like Adobe Premiere Pro have been staples, requiring detailed manual intervention for each editing decision. After AI: AI-powered tools like Runway ML enable automatic video editing by analyzing footage and making smart cuts, transitions, and even optimizing the video for different platforms. This automation saves time and allows editors to concentrate on storytelling and creative aspects of video production. 3. Marketing: AI can analyze customer data to generate personalized advertising content, predict trends, and even optimize marketing strategies in real-time. Before AI: Marketers relied heavily on manual segmentation and trial-and-error methods to target audiences. Campaigns were often designed and revised without real-time data, using platforms like Google Analytics for post-campaign insights. After AI: With AI platforms like Marketo and HubSpot, marketers can now use predictive analytics to identify customer behavior patterns and personalize marketing at scale. AI helps in real-time decision-making and can dynamically adjust marketing strategies to optimize for engagement and conversion. 4. Coding: In software development, AI can write basic code, test software, and even debug programs, which can speed up the development cycle and let developers focus on more complex problems. Before AI: Software development involved writing every line of code manually. Developers would spend considerable time debugging and testing software using integrated development environments (IDEs) like Eclipse and Visual Studio. After AI: Tools like GitHub Copilot use AI to suggest code snippets and entire functions, helping developers write code faster and more efficiently. AI can also help in debugging by suggesting potential fixes and even writing tests, which speeds up the development cycle significantly. 5. Writing and Content Creation: AI can draft articles, scripts, and even books, which can help writers overcome writer’s block and generate ideas more rapidly. Before AI: Writers and content creators would perform extensive research and write each piece from scratch. Tools like Microsoft Word and Google Docs supported basic writing needs but offered limited assistance in content creation. After AI: AI writing assistants like OpenAI’s ChatGPT can generate drafts, suggest edits, and even create content based on specified styles or tones. These tools help writers generate ideas, overcome writer’s block, and ensure grammatical accuracy, allowing them to focus on refining their content to better engage their audience. However, the integration of GenAI in these domains does not signal the end of human creativity. Rather, it marks a shift in the creative process. GenAI acts as a collaborator, not a replacement. It extends the creative capacity of humans, allowing them to explore new artistic territories and conceptual depths. The increasing use of AI in these fields doesn’t eliminate jobs but rather evolves them. Professionals are required to adapt and learn to co-work with AI, leveraging these tools to enhance their productivity and creativity. Human Creativity: Irreplaceable Nuances Human creativity is distinguished by its intricacies and emotional depth. The ability to infuse personal experiences, emotions, and the human condition into art is uniquely human. While GenAI can mimic styles and patterns, it does not possess the consciousness to experience life, which fundamentally shapes artistic expression. Moreover, creativity involves originality and innovation—traits that are driven by a human’s unique perspective on the world. GenAI operates within the confines of the data it has been trained on, which means it can only remix and reinterpret existing knowledge. Humans, on the other hand, can think abstractly and imagine what has never been conceived. Collaboration, Not Competition The future of creativity with GenAI should be viewed as a collaboration. For example, in the film industry, AI can help streamline production processes, manage complex visual effects, and even suggest plot developments based
Strategies to Make Kids Ready to Face Future Job Market Challenges

In today’s fast-changing world, preparing our kids ready for future careers goes beyond traditional education. As parents and educators, we must equip the next generation with skills that transcend textbooks. With automation and artificial intelligence reshaping industries, experts predict that 65% of today’s children will work in jobs that don’t yet exist, highlighting the urgency for adaptable and forward-thinking educational approaches. How to Equip Your Child With Essential Skills for Future Success How to Mold Your Child for the Jobs of the Future Essential Steps Every Parent Should Take Preparing your child for future careers is a significant responsibility, but as a parent, you have the power to profoundly influence their readiness. Here’s an in-depth guide on how to achieve this. Let’s Decode the Future Job Market to Better Prepare Our Kids for Their Careers Conclusion: Equipping your child for future career demands necessitates a comprehensive approach that combines education, practical experience, and a progressive mindset. Enroll them in courses focused on emerging technologies such as robotics, coding, and AI to foster creativity and enhance problem-solving abilities. Moreover, participation in competitions and engagement in interdisciplinary learning are essential to develop adaptability and innovative thinking. This multifaceted strategy prepares your child to successfully navigate and meet the challenges of the future.
What Happens If We Don’t Teach the Application of Generative AI to Our Children?

In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as one of the most transformative forces of our time. From enhancing daily conveniences to revolutionizing entire industries, AI’s impact is profound and far-reaching. Among the myriad of AI technologies, Generative AI stands out for its ability to create – it can generate text, images, music, and even entire virtual environments. This capability not only augments human creativity but also opens up new realms of possibilities in education, entertainment, healthcare, and beyond. As the world becomes increasingly driven by AI, it is crucial to consider how we are preparing the next generation to navigate and thrive in this new reality. The ability to understand and apply Generative AI is rapidly becoming a fundamental skill, much like reading, writing, and arithmetic. However, there is a significant risk that without proactive education and exposure, many children will grow up without the essential knowledge and skills needed to harness the power of this technology effectively. Imagine a future where AI tools are as commonplace as smartphones and computers, where children use AI to aid their learning, fuel their creativity, and solve complex problems. Now, contrast this with a scenario where children are merely passive consumers of AI technology, lacking the understanding and skills to engage with it meaningfully. The gap between these two futures is vast and has profound implications for individual opportunities, societal progress, and ethical standards. In this blog, we will explore the critical reasons why teaching children about the applications of Generative AI is not just beneficial but necessary. 1. Lagging Behind in a Competitive World Generative AI is already influencing job markets globally, with applications in fields as diverse as healthcare, finance, marketing, and entertainment. If children are not exposed to Generative AI, they risk falling behind their peers who are better prepared to navigate and leverage these technologies. This knowledge gap could result in limited career opportunities and reduced competitiveness in an increasingly AI-driven economy. For instance, AI proficiency is becoming a desired skill in many job descriptions, and without this knowledge, future job seekers might find themselves at a disadvantage. 2. Missed Opportunities for Creativity and Innovation Generative AI is not just about technology; it’s also a catalyst for creativity and innovation. AI can assist children in creating music, art, stories, and even game designs, pushing the boundaries of their imagination. Without understanding how to use these tools, they miss out on opportunities to explore new creative processes and contribute to the arts and sciences in novel ways. For example, a child interested in art could use AI to experiment with different styles and techniques, learning more about artistic expression in the process. 3. Lack of Critical Thinking Skills Teaching children about Generative AI goes beyond technical skills; it also involves fostering critical thinking and ethical considerations. Understanding how AI works, its potential biases, and its impact on society helps children develop a critical approach to technology. Without this knowledge, they might become passive consumers of AI-generated content, lacking the ability to question and critically analyze the technology they use. For example, understanding AI bias can help them recognize and challenge unfair algorithms, promoting a more equitable society. 4. Reduced Digital Literacy In a world where digital literacy is becoming as important as traditional literacy, Generative AI plays a crucial role. Knowing how to interact with AI, from chatbots to AI-driven search engines, is essential for effective communication and information retrieval. Children who are not taught about Generative AI might struggle with digital literacy, making it harder for them to access and evaluate information in the digital age. For example, they might not be able to differentiate between AI-generated content and human-created content, leading to misinformation. 5. Unprepared for Ethical and Privacy Challenges Generative AI raises significant ethical and privacy issues. For instance, AI-generated deepfakes can be used maliciously, and AI algorithms can perpetuate biases if not properly managed. By educating children about these challenges, we prepare them to navigate and address ethical dilemmas and privacy concerns. Without this education, children may become vulnerable to misinformation and unethical AI practices. For instance, understanding the implications of data privacy can help them protect their personal information online. 6. Limited Problem-Solving Abilities Generative AI can be a powerful tool for problem-solving. For example, AI can help design efficient algorithms, create new products, and even assist in scientific research. By understanding how to harness AI, children can develop advanced problem-solving skills, essential for tackling complex real-world challenges. Without this knowledge, their ability to innovate and solve problems effectively is diminished. For instance, a child interested in engineering could use AI to simulate and test various designs, enhancing their understanding and capabilities. 7. Disconnect from Technological Advances As AI continues to advance, those without knowledge of Generative AI risk being disconnected from significant technological progress. This disconnect can lead to a lack of engagement and participation in societal and technological discussions, further widening the gap between those who understand AI and those who do not. For example, they might be less likely to participate in discussions about AI ethics or the impact of AI on jobs, limiting their ability to influence future developments. Final Thoughts The application of Generative AI holds immense potential for the future, and it is crucial that we prepare our children to understand and use this technology responsibly and creatively. By integrating AI education into their learning journey, we equip them with the skills to thrive in a tech-driven world, foster their creativity, and develop their critical thinking abilities. Conversely, failing to do so could leave them at a significant disadvantage, both personally and professionally. Let us commit to making Generative AI an integral part of our children’s education, ensuring they are well-prepared to lead and innovate in the future. Fostering AI literacy and responsible use of technology requires collaborative efforts from parents, educators, policymakers, and society at large. By providing resources and support for parents to engage with their children on AI topics,
